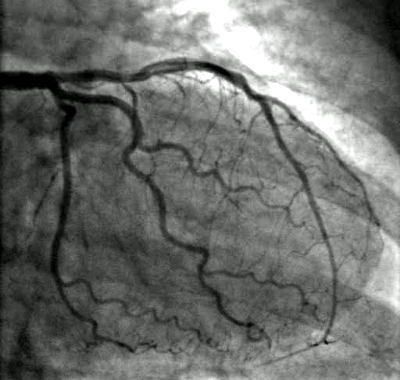
A coronary angiogram is an important diagnostic technique used to elevate heart health, more so the blood vessels that supply the heart. It is used to identify blockages or narrowing of the arteries, which can lead to heart complications.
In the process of the procedure, a small catheter is inserted into a blood vessel, typically through the groin or arm, and contrast dye is injected into the arteries. X-ray imaging is then used to capture detailed images of the heart’s blood vessels, allowing doctors to detect blockages or other abnormalities effectively.
A coronary angiogram is often recommended for patients with experiencing symptoms such as shortness of breath, chest pain, or those who are at high risk of heart disease. This procedure offer important information for diagnosing coronary artery disease and helps doctors develop the ideal treatment plan, such as balloon angioplasty, coronary artery bypass surgery, or stent placement.
Understanding the process of coronary angiogram is essential in making sure you understand what lies ahead. Before the procedure, the patient is advised to avoid eating or drinking for 4-6 hours. A medical history is reviewed, and any medications being taken are looked into.
A catheter is inserted into either the femoral artery or the radial artery with the doctors using local anesthesia to numb the area. Contrast dye is injected into the coronary arteries to make them visible on X-ray images.
Finally, X-ray imaging captures real-time, moving images of the coronary arteries. The doctor evaluates these images to identify any narrowing or blockages. This procedure is typically completed within 30 minutes to an hour, depending on the severity of the case.
As we conclude, it is important to note that acoronary angiogram is performed for several important reasons. For starters, it helps detect conditions such as coronary artery disease (CAD), where the coronary arteries become narrowed or blocked.
If this is not enough, detailed imaging allow doctors to assess the complexity of blockages and plan appropriate treatments. The results of the coronary angiogram help guide decisions on treatments like angioplasty or stent placement.
For patients who have undergone heart interventions, acoronary angiogram helps assess the success of treatments and check for new blockages. It can also reveal other heart problems like heart valve issues or heart muscle abnormalities. While a Coronary Angiogram is a generally safe procedure, there are some risks to be aware of.